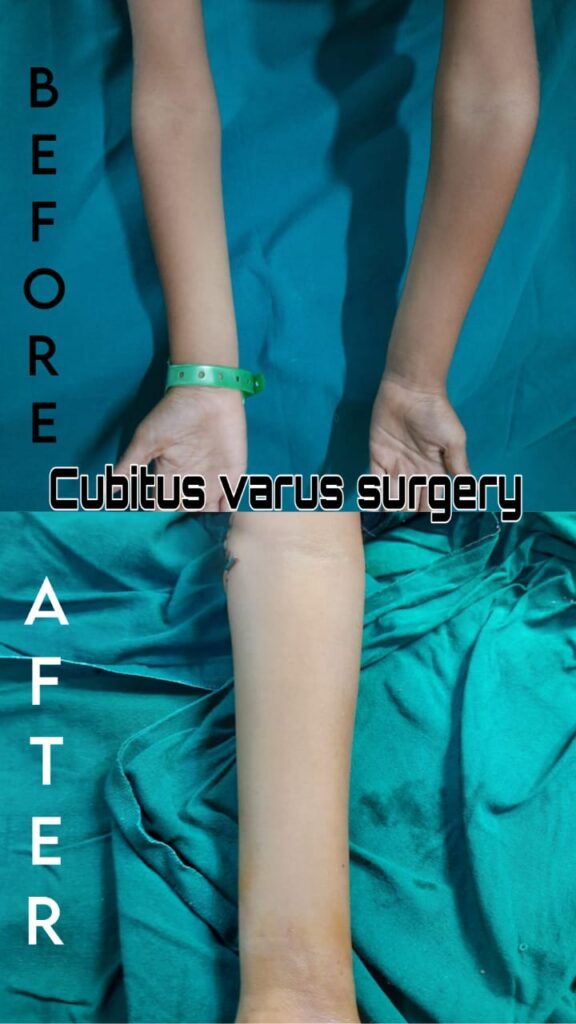
Definition:
Cubitus varus, often referred to as “gunstock deformity,” is a condition where the elbow is deviated inward, causing the arm to angle towards the body when extended. It commonly occurs as a complication of improperly healed fractures, particularly after a supracondylar fracture of the humerus in children.
Causes:
- Malunited fractures: The most common cause is malunion after a supracondylar fracture of the humerus.
- Improper casting or reduction: Inadequate treatment or poor alignment during healing.
- Growth disturbances: Damage to the growth plate in childhood injuries can contribute to the deformity.
- Congenital: Less commonly, cubitus varus can be congenital, present from birth due to bone growth anomalies.
Symptoms:
- Visible deformity: The arm deviates inward when fully extended, creating an abnormal appearance.
- Limited range of motion: In some cases, the elbow may have reduced flexibility or movement.
- Functional limitations: While not always painful, the condition may affect the overall function of the arm, especially during activities requiring full elbow extension.
- Cosmetic concerns: Many individuals are more concerned with the appearance than the function.
Diagnosing:
- Physical examination: Doctors will observe the alignment of the elbow and arm during extension.
- X-rays: Used to assess the bones and the extent of the deformity.
- Angle measurement: The carrying angle of the arm is measured and compared to normal ranges (usually 5-15 degrees of valgus is normal; cubitus varus is a varus or inward deviation).
Treatment:
- Non-surgical options: Generally, there are limited non-surgical treatments for cubitus varus, as bracing or physical therapy is often ineffective in correcting the deformity.
- Surgical correction: The most common treatment is an osteotomy, a procedure where the bone is cut and realigned to restore the normal angle of the arm. Types of osteotomies include:
- Lateral closing wedge osteotomy
- Medial opening wedge osteotomy
- Three-dimensional corrective osteotomy
- Post-surgical care: After surgery, physical therapy is usually required to restore the full range of motion and strength.
Prevention Tips:
- Proper fracture management: Ensuring fractures, especially in children, are treated promptly and properly to prevent malunion.
- Close monitoring during healing: Regular follow-ups after an elbow injury to monitor alignment and healing can help reduce the risk of cubitus varus.
- Early intervention: Addressing improper healing early with corrective measures can prevent long-term deformity.